MOTHERBOARD AND ITS PARTS
| Name | Image | Function |
|---|---|---|
| MOTHERBOARD | A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. | |
| CPU SOCKET | CPU socket is a portion in the motherboard which holds the CPU (Central Processing Unit) or simply the processor | |
| MEMORY(RAM)SLOT | Memory (RAM) Slot is the slot where you will insert the memory module or card. | |
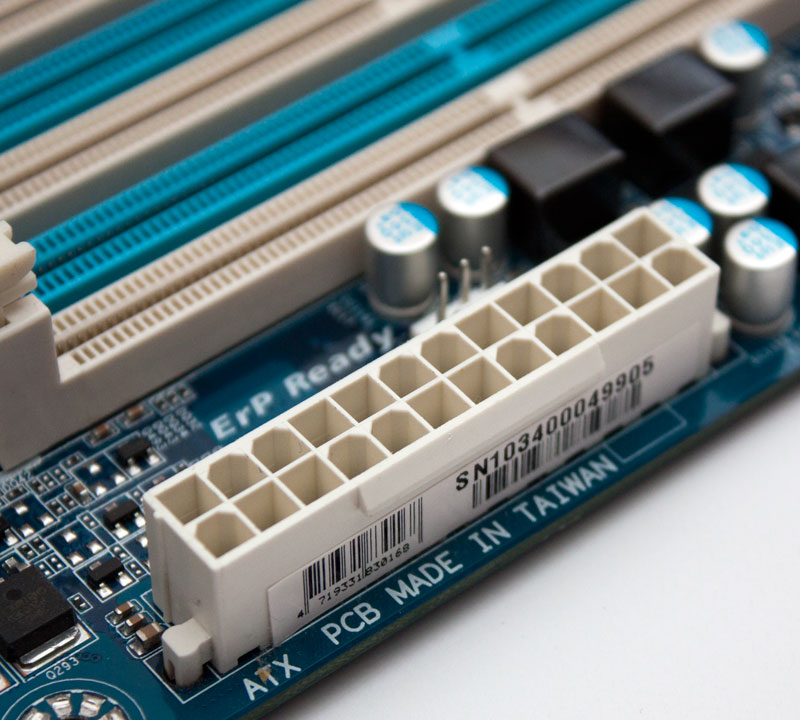
| 24-PIN ATX POWER CONNECTOR | 24-Pin ATX power connector is the portion where you can connect the power supply unit (PSU) power connector. | |
| NORTHBRIDGE CHIP SET | Northbridge Chip set handles the data transfer duties of memory,CPU, and AGP and to make the most efficient use available resources. | |
| CMOS OR BIOS CHIP | CMOS ( Complementary Metal Oxide Semi-conductor) is also achipset which contains the BIOS (Basic Inout Output System).The BIOS is the built in software that tells what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk. | |
| S-ATA PORTS | Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, also known as Serial ATA or SATA, enables mass storage devices, such as hard drives and optical drives, to communicate with the motherboard using a high-speed serial cable over two pairs of conductors. Figure : Example of SATA connections on a hard drive. Power cable. | |
| I/O PORT | (Input/Output port) An I/O port is a socket on a computer that a cable is plugged into. The port connects the CPU to a peripheral device via a hardware interface or to the network via a network interface. See port, standards - hardware interfaces, DisplayPort, HDMI and USB. | |
| PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. | |
| AGP | Accelerated Graphics Port is a parallel expansion card standard, designed for attaching a video card to a computer system to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. | |
| ISA | Industry Standard Architecture is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. | |
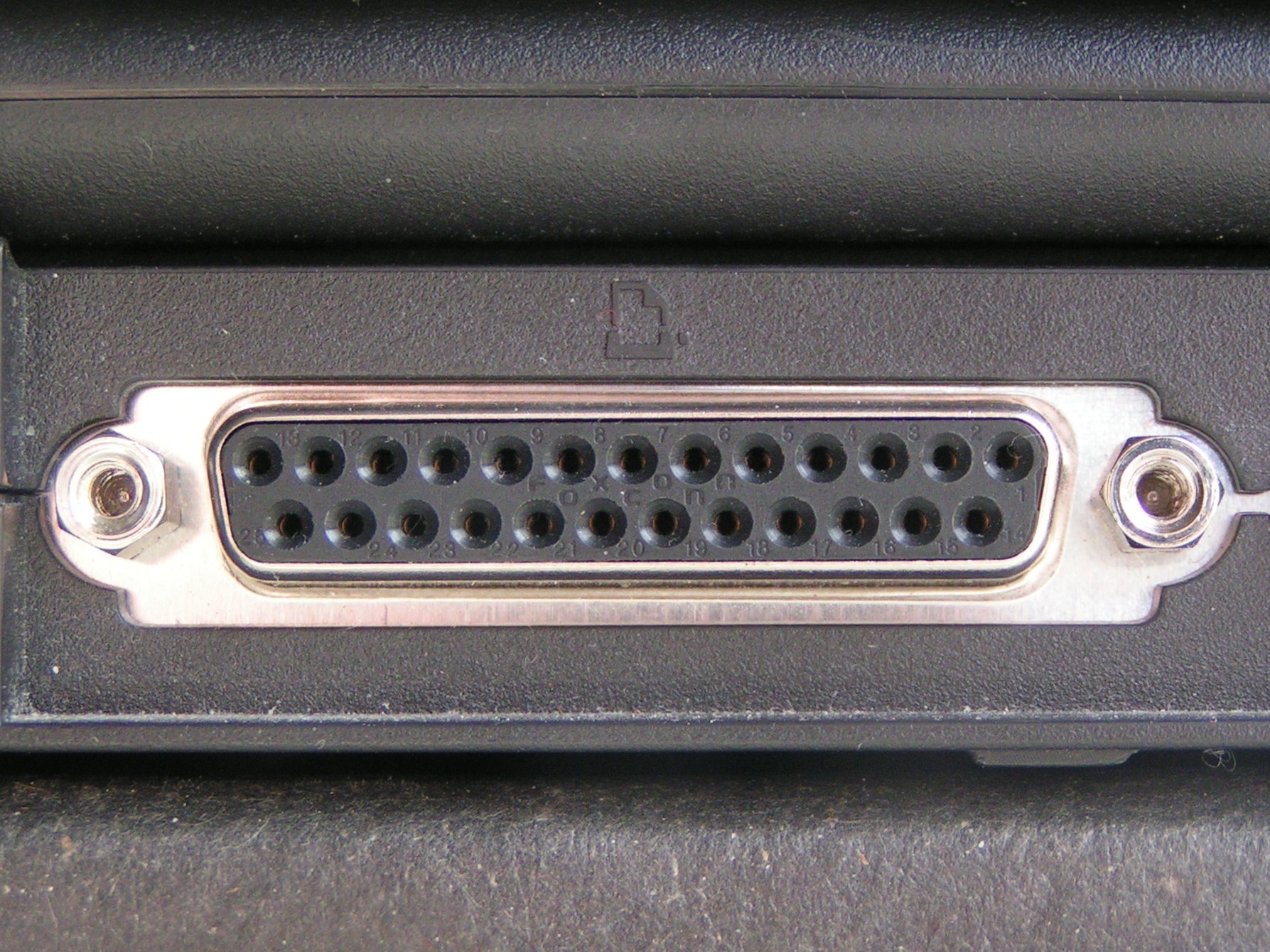
| PARALLEL PORT | Parallel port is a type of interface found on early computers for connecting peripherals. The name refers to the way the data is sent; parallel ports send multiple bits of data at once, as opposed to serial communication, in which bits are sent one at a time. | |
| FDC | A floppy-disk controller has evolved from a discrete set of components on one or more circuit boards to a special-purpose integrated circuit or a component thereof. An FDC directs and controls reading from and writing to a computer's floppy disk drive. | |
| IDE | IDE controller, also known as the ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment) controller, is an asynchronous parallel interface between a host microprocessor system and a standard IDE device. Therefore, this can be called a host adapter because it provides a way to connect a complete IDE device to the host. | |
| POWER SUPPLY CONNECTOR | The ATX 24-pin power supply connector is the standard motherboard power connector in computers today. The connector itself is a Molex 39-01-2240 connector, often called a Molex Mini-fit Jr. | |
| MOUSE AND KEYBOARD PORT | The PS/2 (Personal System/2) port, also referred to as the mouse port or keyboard port, was developed by IBM. It is used to connect a computer mouse or keyboard to an IBM compatible computer. The PS/2 port is a mini DIN plug containing six pins and is still sometimes found on all IBM compatible computers. | |
| HEATSINK | A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. | |
| USB 3.1 Gen1 header | USB 3.1 Gen 1 supports speeds of up to 5Gbit/s while USB 3.1 Gen 2 supports speeds of up to 10Gbit/s. The USB-IF intended to use a set of different names to call the USB 3.1 Gen 1 and USB 3.1 Gen 2 that would've made it better strictly for marketing purposes. | |
| M.2 CONNECTOR | M. 2 connector, formerly known as Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is a type of internal computer connector. It replaces the mSATA standard and allows you to insert small expansion cards on everything from desktop PCs to thin-and-light laptops. | |
| TPM HEADER | Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a microchip attached to the motherboard, is included in some computers. The TPM is also famous as ISO/IEC 11889). It can provide you with great hardware-based cybersecurity. The trusted platform module is designed to be a tamper-resistant store for cryptographic keys. | |
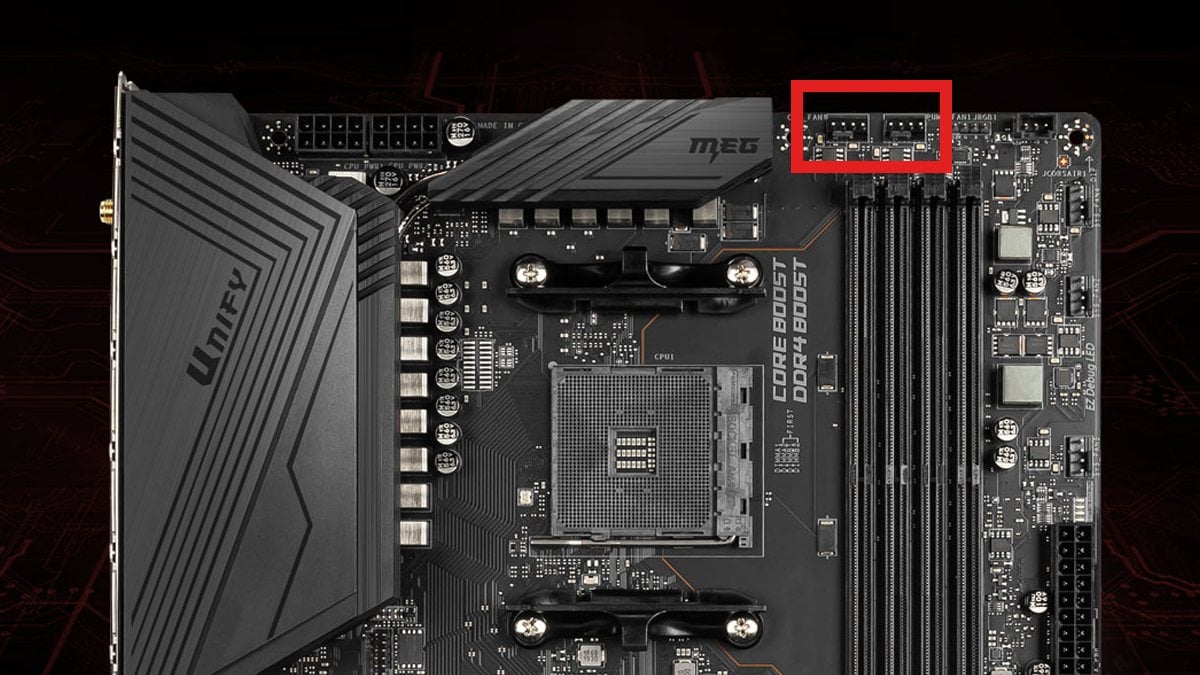
| FAN HEADERS | CPU_FAN headers are used to power the fan of your CPU. They typically have four pins, which means their speed can be adjusted based on the CPU temp data, either through dedicated software, BIOS, or the operating system itself. |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)